Ecommerce fulfilLment services
Warehouse Management
Streamlined inbound process and an extensive network for the efficient distribution of your goods.
Order Pick & Pack
Expert handling for fast, accurate operations that speed up delivery to your customer.
Inventory Management
Real-time visibility into stock levels for constant order processing and supply chain flexibility.
Seamless Shipping & Returns
Automatically assign couriers based on order value or destination to last-mile, with branded return solutions for enhanced customer satisfaction.
Global B2B Fulfillment
Delivering efficiency for your retail order and distribution processes across international markets.
Next Day Shipping
Localised centre for fast and reliable shipping, with various delivery methods at a competitive price.
3PL Teams
Access trusted partners for expert localised logistics solutions and support for any delivery destination.
Parcel Handover
Receive real-time tracking, ensuring transparency and peace of mind for every step of the delivery process.
Multi-Channel Integrations
Convenient connections to existing systems and sales channels including Shopify and Amazon.
Simplify your e-commerce operations

Fulfillment Services
Warehousing, picking & packing, shipping, and returns, as well as value added services.

Product Stock management
A single source of truth across all fulfillment centers, allowing you to track your inventory in real-time.
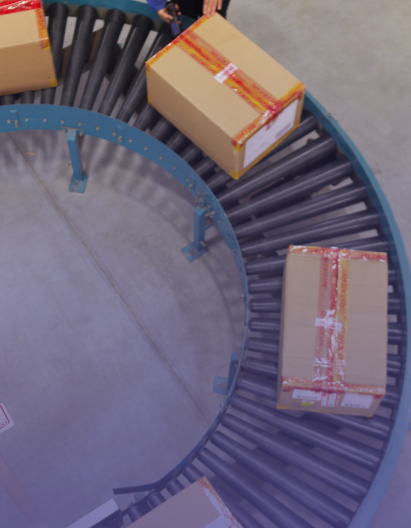

Multi-channel integration
Connecting you to major e-commerce platforms and marketplaces.
How it works
Make shipping and fulfillment stress-free, so you can focus on your reach and grow your business.
Why do you need a fulfillment service ?

Scale your business and sell globally
Use our strategically located fulfillment centres to expand your sales to the new markets.

Unlock the 2-day shipping
Optimal inventory split across our growing fulfillment network improving delivery speed and shipping cost.

Seamless integration and orders management across channels
Improve tracking and deliveries, get insights easily, and speed up starting, with pre-built connections, helping you provide a consistent customer experience.
Get in touch
Fill out our form, we’ll help you ship and sell everywhere to grow faster.
The DP World Group (our different companies can be found at DP World) would like to use the above personal data, to send you information about our products and services via any of these channels: email, telephone, WhatsApp, SMS and social media (such as LinkedIn). By clicking submit, you consent to us processing your personal data in this manner. You can opt out at any time by clicking here Privacy Policy, or by hitting the “unsubscribe” button at the bottom of our emails.